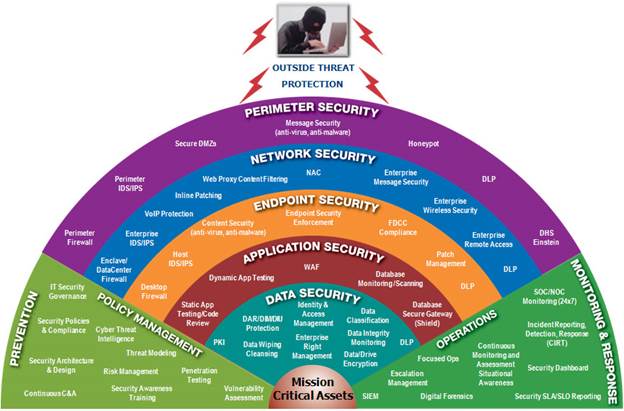
One of the most efficient ways to deal with security issues in general and
information security in specific is to apply a layered based model in order to be
able to understand threats and apply necessary countermeasures for it.
What makes this model suitable for security is the architecture of network and
information systems nowadays where most of the interactions are between
users and information systems through the network as a set of requests sent
from the beneficiary to the server that will handle the request, process any sent
information, retrieve or manipulate data.in that context the data become the core
of model as it is the main important asset that need to be protected.
Many models were created to embody the layered security approach from
different perspectives.
Some models took in consideration the security policy and user dimension and
other focus more on the main layers:
1 The Physical layer:
We mean by the physical layer the direct physical access to hardware. As
illustrated in the chart above the access to the physical layer can be very
direct and dangerous because attacker can cause direct damage or
compromise network, processing, and storage devices. As example
causing a denial of service that work on a server is simply doable by
unplugging the power cord of that server. This is why physical security of
data centers is an issue that needs to be taken seriously.
A well designed architecture should allow response to attack even with
physical based attacks as example sending notification or raising an alarm.
2 Network Layer:
When the attacker doesn’t have any direct access to the physical
hardware the only available path is through external layers toward the
core where the data assets resides.
Compromising network layer will make it easy for attacker to disclose,
alter, or make unavailable mainly the data in motion sent by legitimate
user or response sent by the server. Network layer in that model
represent all activities, devices and protocols used to transfer data from
its source to destination.
3 Platform layer:
The platform layer represents the carrier of application layer it provides the
interface between hardware devices and the application layer in addition to
process and file management.
This layer is normally reflected through operating system and any used
framework or server software that host the application.
4 Application layer:
This layer represents all input processing, storage, retrieval,
manipulation and output activities done on server side or client side.
This layer depends on services it gets from the platform layer.
5 Data layer:
This is the layer where the precious assets reside, as it is known that the
Data is the real asset in information systems.
If an attacker is able to reach this layer the information system is
considered as compromised.
6 The response layer:
This layer is the deepest layer it encompasses all Data and system
recovery, monitoring, logging and notification activities.
This layer safety is critical because it is the only guarantee that the data
will be partially or totally recovered after an attack or at least knowing
that the attack took place.
Response layer is an abstract layer because its contents might be
distributed over network, platform and application layer
The security of layers:
in a layer based model each layer provides services to the next layer in order.
one of the provided services is security thus each layer is responsible of
preventing any malicious attack from passing through to the next layer.but since
layers hold different nature it is sometime impossible for a specific layer to stop
an attack that ment to target deeper layer.lot of malicious requests can travel
freely without any problem through a specific layer as a legitimte requests
because request does not contain any sign of malicious activity related to that
layer.
Attacker might need to compromise more than one layer to be able to fulfill the
attack goals. Compromising a layer is not always the goal of attack it might be
only a step to compromise deeper layer to realize the target of attack.
The following drawing illustrates some examples of attack scenarios:
Application layer security
Application layer as mentioned is the layer where all the logic of input,
processing, manipulation, storage and output reside that makes this layer the
place containing the customized component thus the components with less
maturity which makes it the most tempting to malicious attacks.


0 comments: